Welcome to the blood type mystery answer key, where the enigmatic world of blood types unravels before your eyes. From health implications to personality traits, from evolutionary history to forensic applications, we’ll delve into the fascinating tapestry of blood types, revealing the hidden truths that lie within.
Join us on this captivating journey as we explore the intriguing connections between blood types and our physical, psychological, and even historical makeup. Prepare to be amazed as we unlock the secrets of your blood, one fascinating discovery at a time.
Introduction to Blood Type Mystery
Blood types are inherited characteristics that play a crucial role in medicine, particularly in blood transfusions. Understanding blood types and their inheritance patterns is essential to ensure safe and compatible transfusions.
The ABO blood group system, discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901, classifies blood into four main types: A, B, AB, and O. These types are determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens (A and B) on the surface of red blood cells.
The Rh Factor
In addition to the ABO system, the Rh factor is another important blood group antigen. People with the Rh factor are Rh-positive, while those without it are Rh-negative. The Rh factor is also inherited and can affect blood transfusion compatibility.
Blood Type and Health Implications
The presence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells categorizes individuals into different blood types. These antigens interact with antibodies in the immune system, playing a crucial role in blood compatibility and immune responses. Beyond blood transfusions, blood type has been linked to various health conditions and implications.
Association with Diseases and Disorders
Studies have revealed correlations between certain blood types and increased susceptibility or resistance to particular diseases and disorders. For instance, individuals with blood type O are less likely to develop malaria, while those with blood type A are more prone to stomach ulcers.
Additionally, blood type B has been associated with an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer. Conversely, blood type AB is linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases.
While exploring the mysteries of blood types can be fascinating, take a break and immerse yourself in the verdant world of trees and plants word stacks . This engaging game challenges you to connect words related to the plant kingdom.
Once you’ve unraveled the intricacies of both trees and blood types, you’ll appreciate the interconnectedness of all living things.
Role in Organ Transplantation and Blood Donation
In organ transplantation, matching the blood type between the donor and recipient is crucial for successful outcomes. Incompatible blood types can lead to rejection of the transplanted organ due to an immune response against foreign antigens.
Similarly, blood donation also considers blood type compatibility. Individuals with blood type O are known as universal donors as their red blood cells lack specific antigens, making them compatible with recipients of all blood types. Conversely, individuals with blood type AB are universal recipients as they possess both A and B antigens, allowing them to receive blood from any blood type.
Blood Type and Personality Traits

The relationship between blood type and personality traits has been a subject of fascination and debate for decades. While some studies suggest that certain blood types may be associated with specific personality characteristics, the scientific evidence supporting these claims remains inconclusive.
Cultural and Societal Implications
Despite the lack of scientific consensus, the idea that blood type can influence personality has gained popularity in some cultures. In Japan, for example, blood type personality theories have been widely embraced and used in various aspects of life, such as career choice, dating, and even medical treatment.
However, it is important to note that these theories have no basis in scientific research and should not be used to make important life decisions. Blood type is determined by genetic factors and does not have any direct impact on an individual’s personality or behavior.
Blood Type and Evolutionary History
Blood types have evolved over millions of years as humans adapted to different environments and migrated across the globe. The distribution of blood types among populations provides valuable insights into our evolutionary history.
Origins of Blood Types
The earliest known blood types emerged in primates around 20 million years ago. As humans evolved, distinct blood group systems, including the ABO and Rh systems, developed through genetic mutations.
Influence of Human Migration and Adaptation
As humans migrated and adapted to new environments, natural selection played a role in shaping blood type diversity. For example, in malaria-prone regions, the Duffy antigen, present on red blood cells of individuals with Duffy-positive blood types, provided protection against the parasite. This led to a higher prevalence of Duffy-positive blood types in these areas.
Role in Survival and Spread of Populations
Blood type may have influenced the survival and spread of different populations. In certain cases, specific blood types conferred advantages in specific environments. For example, in areas with high levels of infectious diseases, certain blood types may have provided resistance or susceptibility to certain pathogens, influencing the survival and growth of populations with those blood types.
Blood Type and Forensics: Blood Type Mystery Answer Key
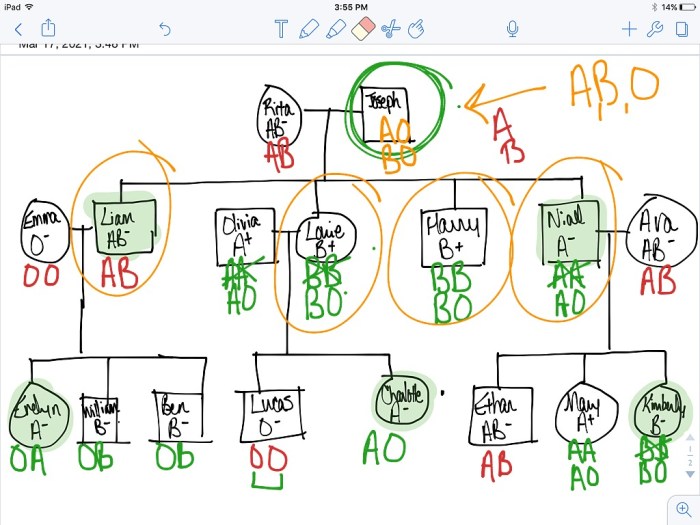
Blood type analysis plays a vital role in forensic investigations. By examining the blood type of evidence found at a crime scene, investigators can narrow down the list of potential suspects and even identify individuals.
Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. These antigens are inherited from both parents, and each individual has a unique blood type combination.
Identifying Individuals
Blood type analysis can be used to identify individuals in a variety of situations, including:
- Crime scene investigations: Blood type can be used to identify victims or suspects from bloodstains or other bodily fluids found at the scene.
- Missing persons cases: Blood type can be used to identify remains or to rule out potential matches.
- Paternity testing: Blood type can be used to determine whether a man is the biological father of a child.
Determining Paternity
Blood type analysis is a valuable tool for determining paternity. By comparing the blood types of the mother, child, and alleged father, it is possible to determine whether the alleged father could be the biological father.
For example, if the mother has blood type A and the child has blood type AB, the alleged father must have blood type A or AB. If the alleged father has blood type O, he cannot be the biological father.
Limitations and Ethical Considerations, Blood type mystery answer key
While blood type analysis is a powerful tool in forensic investigations, it does have some limitations.
- Blood type is not unique to an individual. There are many people who share the same blood type, so it is not always possible to identify a specific individual based on blood type alone.
- Blood type can change over time. Certain diseases and conditions can affect blood type, so it is important to consider the possibility that a person’s blood type may have changed since the time of the crime.
There are also some ethical considerations to keep in mind when using blood type analysis in forensics.
- Privacy: Blood type is a personal identifier, so it is important to protect the privacy of individuals whose blood type is being analyzed.
- Discrimination: Blood type has been used in the past to discriminate against certain groups of people. It is important to ensure that blood type analysis is not used for discriminatory purposes.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the most common blood type?
O positive is the most common blood type, found in approximately 37% of the world’s population.
Can I donate blood to anyone with the same blood type?
Not necessarily. While blood type compatibility is a crucial factor, other factors such as the Rh factor and minor blood group antigens also play a role in determining compatibility.
Is there a link between blood type and personality?
While some theories suggest a correlation between blood type and personality traits, scientific evidence supporting these claims remains inconclusive.