Atp adp cycle worksheet answers – Embark on a journey into the enigmatic world of ATP-ADP cycle worksheet answers, where the secrets of cellular energy transfer unfold. Dive into the intricate workings of this vital cycle, exploring its components, reactions, and profound implications for life as we know it.
Unravel the fundamental principles governing the ATP-ADP cycle, tracing its historical roots and unraveling its significance in maintaining the delicate balance of cellular processes.
ATP-ADP Cycle Overview
The ATP-ADP cycle is a fundamental process in cellular metabolism that involves the interconversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This cycle plays a crucial role in energy transfer within cells, providing the energy necessary for various cellular processes.
Discovery and Significance
The ATP-ADP cycle was first discovered by German biochemist Otto Warburg in the 1920s. Warburg’s research revealed the importance of ATP as an energy currency in cells, and he proposed the concept of the ATP-ADP cycle as a means of energy transfer.
The significance of the ATP-ADP cycle lies in its central role in cellular energy metabolism. ATP serves as the primary energy currency for cells, providing the energy required for a wide range of cellular activities, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and chemical synthesis.
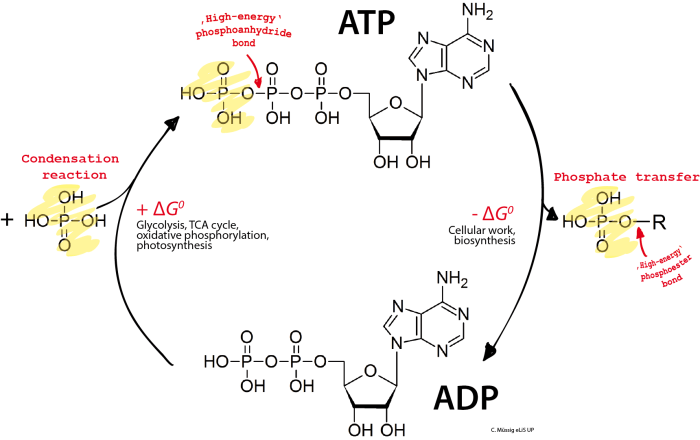
Key Components and Reactions
The ATP-ADP cycle is a fundamental process in cellular energy metabolism. It involves the interconversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP), releasing or consuming energy in the process. Several key components and reactions are involved in this cycle.
Key Components, Atp adp cycle worksheet answers
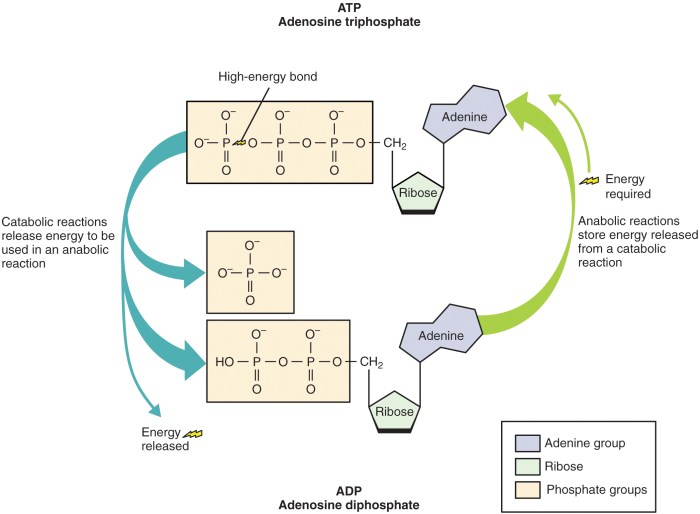
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate):A nucleotide consisting of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. ATP is the primary energy currency of cells, providing energy for various cellular processes.
- ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate):A nucleotide consisting of adenine, ribose, and two phosphate groups. ADP is the product of ATP hydrolysis and can be converted back to ATP to replenish the energy supply.
- Enzymes:Proteins that catalyze and facilitate the reactions in the ATP-ADP cycle, including ATP synthase, ATPase, and kinases.
Chemical Reactions
The ATP-ADP cycle involves two main chemical reactions:
- ATP Hydrolysis:ATP is broken down into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), releasing energy. This reaction is catalyzed by ATPase enzymes and provides energy for cellular processes.
- ATP Synthesis:ADP is converted back into ATP by adding a phosphate group from Pi, consuming energy. This reaction is catalyzed by ATP synthase enzymes and regenerates ATP for cellular use.
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + Energy
ADP + Pi + Energy → ATP
Energy Transfer and Storage
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) plays a crucial role in energy transfer and storage within cells. It acts as the primary energy currency, facilitating the exchange of energy between different cellular processes.
After finishing the ATP ADP cycle worksheet answers, you might want to take a break and learn about something completely different, like the hydra ram forcible entry tool . It’s a fascinating device used by law enforcement and emergency responders.
When you’re ready to get back to your studies, the ATP ADP cycle worksheet answers will still be waiting for you.
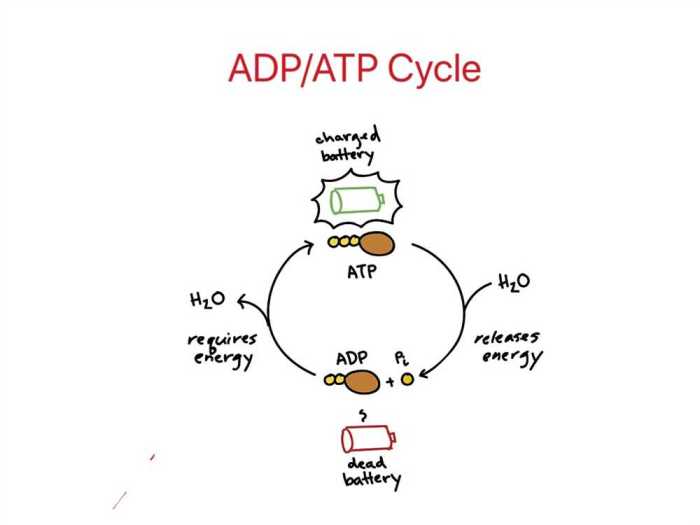
The ATP-ADP cycle involves the interconversion of ATP and ADP (adenosine diphosphate). During energy-requiring processes, ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP, releasing energy that can be utilized by the cell. Conversely, during energy-producing processes, ADP is phosphorylated to form ATP, storing energy for future use.
ATP as the Energy Currency
- ATP is a high-energy molecule, containing three phosphate groups attached to a ribose sugar and an adenine base.
- The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases a significant amount of energy, approximately 7.3 kcal/mol.
- This energy is used to drive various cellular processes, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and chemical synthesis.
ATP-ADP Cycle
- The ATP-ADP cycle is a continuous process that maintains the cellular energy balance.
- During energy-requiring processes, ATP is hydrolyzed by enzymes called ATPases, releasing ADP and energy.
- The ADP is then rephosphorylated to form ATP through energy-producing processes, such as oxidative phosphorylation and substrate-level phosphorylation.
Regulation of the ATP-ADP Cycle
The ATP-ADP cycle is tightly regulated to maintain cellular homeostasis and energy balance. Several factors influence the rate and efficiency of the cycle, ensuring that ATP levels meet the metabolic demands of the cell.
Key Regulators
- ATP concentration:High ATP levels inhibit glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, slowing down the production of ATP.
- ADP concentration:Increased ADP levels stimulate glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation, increasing ATP production.
- Phosphofructokinase (PFK-1):This enzyme catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycolysis. It is allosterically activated by ADP and inhibited by ATP, regulating the flux of glucose into the glycolytic pathway.
- Pyruvate kinase (PK):This enzyme catalyzes the final step of glycolysis. It is allosterically activated by ADP and inhibited by ATP, controlling the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate.
- Mitochondrial ATPase:This enzyme hydrolyzes ATP to produce ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). It is regulated by the proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane, influencing the rate of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production.
Importance of Maintaining ATP Levels
Maintaining adequate ATP levels is crucial for cellular function. ATP is the primary energy currency of the cell, providing energy for essential processes such as muscle contraction, ion transport, and protein synthesis. Dysregulation of the ATP-ADP cycle can lead to cellular dysfunction and disease.
Clinical Significance
The ATP-ADP cycle is fundamental to various physiological processes, and disruptions in its normal functioning can have significant clinical implications.
Dysregulation of the ATP-ADP cycle has been associated with a range of diseases and disorders, including:
Mitochondrial Disorders
- Mitochondrial diseases, characterized by impaired oxidative phosphorylation, can disrupt ATP production, leading to energy depletion and cellular dysfunction.
Neurological Disorders
- Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s involve disruptions in energy metabolism, affecting ATP production and utilization within neurons.
Metabolic Disorders
- Inborn errors of metabolism can impair ATP synthesis or utilization, leading to metabolic imbalances and developmental disorders.
Therapeutic Applications
Understanding the ATP-ADP cycle holds therapeutic potential for various diseases:
Mitochondrial Disorders
- Strategies aimed at enhancing mitochondrial function and ATP production could mitigate symptoms of mitochondrial disorders.
Neurological Disorders
- Therapeutic interventions targeting energy metabolism and ATP homeostasis could provide neuroprotective benefits in neurodegenerative diseases.
Metabolic Disorders
- Enzyme replacement therapy or gene therapy could correct metabolic defects that disrupt the ATP-ADP cycle in inborn errors of metabolism.
Worksheet Analysis
The worksheet questions and their corresponding correct answers and explanations are presented in the table below:
| Worksheet Questions | Correct Answers | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
| What is the role of ATP in the cell? | ATP is the primary energy currency of the cell and provides energy for various cellular processes. | ATP serves as the primary source of energy for cellular activities, powering processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and chemical reactions. |
| Describe the process of ATP hydrolysis. | ATP hydrolysis involves the breakdown of ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), releasing energy in the process. | ATP hydrolysis is a fundamental reaction in energy metabolism, where ATP is broken down to release energy, providing the driving force for cellular processes. |
| How is ATP synthesized in the cell? | ATP synthesis occurs through various pathways, including glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and substrate-level phosphorylation. | The synthesis of ATP involves multiple mechanisms, such as glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm, and oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the mitochondria. |
| Explain the regulation of the ATP-ADP cycle. | The ATP-ADP cycle is regulated by various mechanisms, including feedback inhibition and allosteric regulation. | Feedback inhibition and allosteric regulation play crucial roles in controlling the ATP-ADP cycle, ensuring an appropriate balance of energy production and utilization. |
| Discuss the clinical significance of the ATP-ADP cycle. | Dysregulation of the ATP-ADP cycle can lead to various pathological conditions, including muscle disorders and metabolic diseases. | Understanding the ATP-ADP cycle is essential in clinical settings, as its dysregulation can manifest in various diseases, highlighting its importance in maintaining cellular health and overall well-being. |
Frequently Asked Questions: Atp Adp Cycle Worksheet Answers
What is the significance of the ATP-ADP cycle?
The ATP-ADP cycle plays a pivotal role in cellular energy transfer, providing the energy currency for a multitude of cellular processes.
How does the ATP-ADP cycle regulate cellular function?
The ATP-ADP cycle is tightly regulated to maintain optimal cellular function, ensuring a steady supply of energy for essential processes.
What are the clinical implications of disruptions in the ATP-ADP cycle?
Disruptions in the ATP-ADP cycle can lead to various diseases and disorders, highlighting its critical role in maintaining cellular health.