As we delve into the realm of match each post-impressionist with a feature of his style, we embark on a journey that unveils the distinctive characteristics that define this groundbreaking art movement. Post-Impressionism emerged as a revolutionary force, challenging the conventions of Impressionism and paving the way for new modes of artistic expression.
This artistic movement was characterized by a profound shift towards subjective interpretation, emotional expression, and the exploration of form and structure. Post-Impressionist artists sought to convey not merely the visual appearance of the world but also their inner emotions and perspectives, leading to a remarkable diversity of styles and techniques.
Post-Impressionism and Its Features
Post-Impressionism emerged in the late 19th century as an art movement that rejected the fleeting and momentary focus of Impressionism. Instead, Post-Impressionists sought to explore deeper emotional and symbolic content through their works.
Key characteristics of Post-Impressionism include:
- Emphasis on structure and form over light and color
- Use of bold colors and exaggerated brushwork
- Exploration of symbolism and allegory
Post-Impressionism paved the way for the development of modern art and influenced subsequent movements such as Cubism, Expressionism, and Fauvism.
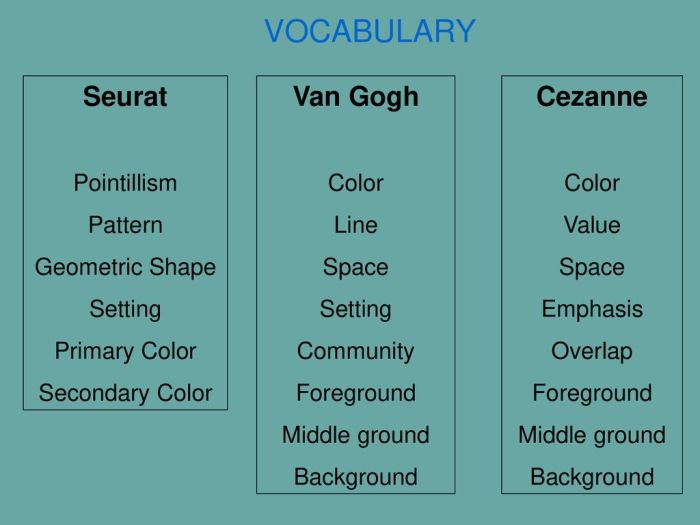
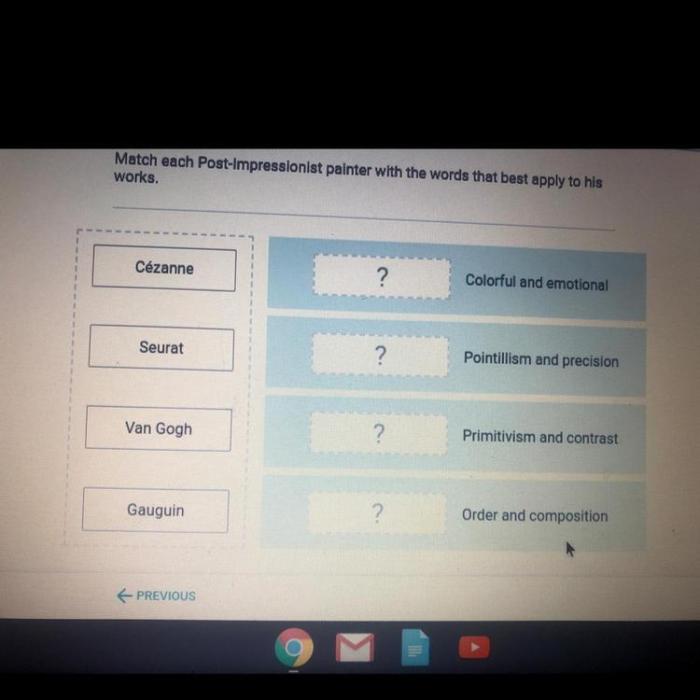
Georges Seurat: Pointillism, Match each post-impressionist with a feature of his style
Georges Seurat mengembangkan teknik Pointillism, di mana ia menerapkan titik-titik warna kecil secara berdekatan untuk menciptakan ilusi warna dan kedalaman.
Pointillism memungkinkan Seurat untuk menciptakan:
- Gradasi warna yang halus
- Rasa getaran dan luminositas
- Komposisi yang sangat terstruktur
Contoh karya Pointillis Seurat antara lain “A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte”dan “The Circus.”
Paul Cézanne: Geometric Forms
Paul Cézanne dikenal karena penggunaan bentuk-bentuk geometris untuk menyederhanakan dan menata komposisinya.
Cézanne percaya bahwa semua bentuk di alam dapat disederhanakan menjadi bentuk dasar seperti kerucut, bola, dan silinder.
Pendekatan Cézanne memengaruhi perkembangan Cubism, sebuah gerakan yang memecah bentuk menjadi bidang-bidang geometris.
Contoh karya Cézanne yang menunjukkan penggunaan bentuk geometrisnya antara lain “Mont Sainte-Victoire”dan “The Card Players.”
Vincent van Gogh: Expressionism
Vincent van Gogh adalah pelopor Ekspresionisme, sebuah gerakan yang menekankan ekspresi emosi melalui warna dan sapuan kuas yang intens.
Karya-karya van Gogh ditandai dengan:
- Warna-warna cerah dan berapi-api
- Sapuan kuas yang dinamis dan berputar
- Ekspresi emosi yang mendalam dan mentah
Contoh karya Ekspresionis van Gogh antara lain “The Starry Night”dan “Sunflowers.”
Henri Matisse: Fauvism
Henri Matisse adalah pemimpin gerakan Fauvisme, yang menekankan penggunaan warna-warna cerah dan bentuk-bentuk yang disederhanakan.
Fauvisme dicirikan oleh:
- Warna-warna yang tidak realistis dan tidak alami
- Bentuk-bentuk yang disederhanakan dan rata
- Penggunaan garis yang ekspresif
Karya Matisse yang menunjukkan karakteristik Fauvisme antara lain “The Green Stripe”dan “Woman with a Hat.”
Paul Gauguin: Symbolism
Paul Gauguin adalah seorang pelopor Simbolisme, sebuah gerakan yang menggunakan simbol dan alegori untuk mengekspresikan makna yang lebih dalam.
Karya Gauguin sering menggambarkan tema-tema spiritual dan mistis, serta budaya non-Barat.
Contoh karya Simbolis Gauguin antara lain “The Yellow Christ”dan “Tahitian Women on the Beach.”
FAQ Resource: Match Each Post-impressionist With A Feature Of His Style
What are the key characteristics of Post-Impressionism?
Post-Impressionism is characterized by a focus on subjective interpretation, emotional expression, and the exploration of form and structure.
How did Post-Impressionism differ from Impressionism?
Post-Impressionism moved beyond the emphasis on capturing the fleeting effects of light and atmosphere that defined Impressionism, instead exploring more profound and subjective aspects of the world.
Who are some of the most famous Post-Impressionist artists?
Georges Seurat, Paul Cézanne, Vincent van Gogh, Henri Matisse, and Paul Gauguin are among the most renowned Post-Impressionist artists.